In the world of electronics manufacturing and micro-assembly, precision and consistency are everything. With devices becoming increasingly compact, traditional soldering techniques are often unable to meet the demand for accuracy and speed. That’s where Laser Soldering Machines 🌟 come into play. They offer a clean, efficient, and contactless method of joining components on circuit boards — and they’re transforming industries in the process.
Let’s dive deep into the fascinating world of laser soldering, its applications, advantages, and why it might just be the future of electronics assembly.
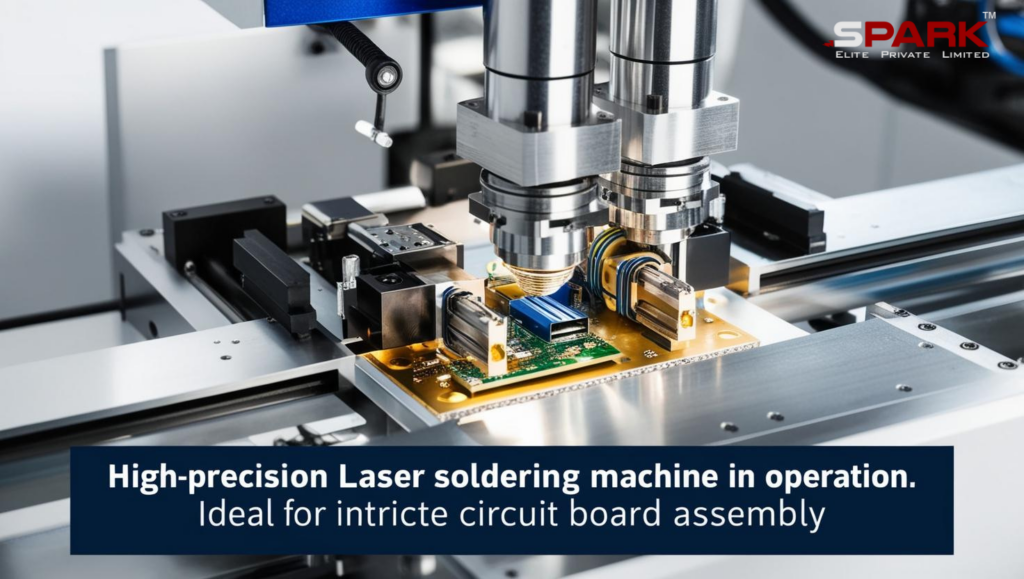
What Is a Laser Soldering Machine?
A laser soldering machine is an advanced tool that uses a focused beam of laser light 🎯 to heat and melt solder material for joining electronic components. Unlike traditional methods that use soldering irons or hot air, a laser soldering system offers non-contact heating, making it ideal for delicate and miniature components.
⚙️ How It Works:
- Laser Generation: A laser beam (often from a diode or fiber laser) is generated and focused through optics onto the solder joint.
- Localized Heating: The beam rapidly heats the solder pad and wire/component lead to the desired temperature.
- Controlled Process: Parameters like power, time, and beam diameter are precisely controlled via software, ensuring uniform solder joints.
This process is automated, highly repeatable, and suitable for high-speed production lines 🏭.
✅ Advantages of Laser Soldering
Laser soldering has been adopted widely due to its numerous benefits, especially in high-precision environments. Here are some key advantages:
1. Precision and Accuracy
The focused laser beam allows for pinpoint accuracy. This is crucial in microelectronics, medical devices, and compact sensors where traditional soldering tools cannot reach.
2. Speed and Efficiency
Laser soldering is extremely fast. Solder joints can be completed in milliseconds, which drastically increases throughput in manufacturing.
3. Clean and Contactless Process
No physical contact means there is minimal risk of damaging sensitive components. Also, the process doesn’t produce smoke or flux residues, maintaining a clean working environment.
4. Automation-Ready
Most laser soldering systems are compatible with robotic arms 🤖 or integrated into production lines, allowing for hands-free, automated soldering.
5. Consistency and Repeatability
Because it is software-controlled, each solder joint can be exactly replicated. This leads to higher quality assurance and less manual error.
🛠️ Components of a Laser Soldering System
A typical laser soldering machine includes several key components:
- Laser Source (Diode/Fiber/CO2)
- Beam Delivery System (lenses, mirrors)
- Control Software 🖥️
- Motion System (robotic arms or gantry)
- Vision System (for alignment and inspection) 👁️
- Cooling System (air or water-based)
Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the machine works efficiently and safely.
🧪 Applications of Laser Soldering
Laser soldering machines are used in a wide range of industries, including:
Consumer Electronics
Used for assembling smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable tech where components are tightly packed.
Automotive Electronics
Critical in producing robust and vibration-resistant joints in sensors, ECUs, and control modules.
Medical Devices
Laser soldering is perfect for joining tiny components in hearing aids, pacemakers, and diagnostic devices with minimal heat impact.
Aerospace and Defense
High-reliability joints are essential in mission-critical systems — laser soldering offers the reliability and quality required.
Telecommunications
Fiber optic connectors, RF modules, and antenna assemblies often require laser-based precision soldering.
Why Choose Laser Over Traditional Soldering?
Traditional soldering techniques like hand soldering, wave soldering, or reflow have their place. But when you’re dealing with:
- Ultra-miniature components 🧩
- Heat-sensitive materials 🌡️
- High-mix, low-volume production ⚙️
- Need for cleanroom conditions 🧼
…laser soldering becomes the superior option.
Types of Lasers Used in Soldering
Different types of lasers can be used depending on the application:
Diode Lasers
Most common for electronics; compact, energy-efficient, and suitable for most soldering tasks.
Fiber Lasers
Used when higher power and deeper penetration are needed. Excellent for high-speed industrial applications.
CO2 Lasers
Not commonly used for microelectronics, but can be effective in specific materials.
📋 Key Parameters in Laser Soldering
To get perfect joints every time, these parameters must be controlled:
- Laser Power (W)
- Beam Diameter (mm)
- Soldering Time (ms)
- Wavelength (nm)
- Focus Position
Modern systems allow engineers to create custom soldering profiles 👨💻 to optimize these parameters for each component.
⚠️ Challenges and Considerations
Laser soldering isn’t without its challenges:
Cost
Initial setup costs can be high, especially for automated systems. However, the ROI is often justified by the quality and speed gains.
Alignment
Precise alignment is critical. Even minor deviations can cause poor joints or missed targets.
Material Compatibility
Some solders or substrates may reflect or absorb laser light inefficiently. Careful material selection and testing is important.
Process Monitoring
Because it’s non-contact and often invisible (infrared lasers), real-time monitoring systems (like cameras or pyrometers) are often required.
🧠 Smart Features in Modern Laser Soldering Machines
Today’s machines aren’t just tools — they’re smart systems designed for Industry 4.0. Here are some intelligent features you might find:
- AI-Based Quality Control 🧠
- Real-Time Process Monitoring 🔬
- Remote Diagnostics and Updates 🌐
- Integration with MES/ERP Systems
- Data Logging for Traceability 📊
These features allow manufacturers to optimize production, reduce defects, and maintain traceability.
Safety Considerations
Laser systems can be hazardous if not properly shielded and controlled. Key safety features include:
- Enclosures with interlocks 🛡️
- Laser protective glass/shields
- Fume extraction systems (if flux is used) 💨
- Emergency stop controls
- Operator training and PPE 😷
🔄 Maintenance and Lifespan
Laser soldering machines are known for their long service life and low maintenance requirements. Preventive maintenance typically includes:
- Optics cleaning 👓
- Cooling system checks ❄️
- Software updates 💾
- Calibration of motion systems
With proper care, these machines can function reliably for many years — especially in clean, climate-controlled environments.
🌍 Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Laser soldering is considered a greener technology compared to traditional methods:
- No consumables like tips or solder pots ♻️
- Minimal flux = fewer emissions 🌿
- Lower power consumption in many cases
- Less waste due to high precision
This makes laser soldering a favorite in eco-conscious manufacturing setups.
🔚 Conclusion: Is Laser Soldering the Future?
Absolutely! ✅
Laser soldering machines are becoming indispensable in precision-driven industries. With increasing miniaturization 📉, demand for quality 🥇, and the push for automation 🔄, they offer the perfect combination of speed, consistency, and cleanliness.
Whether you’re in electronics, automotive, medical, or aerospace, investing in laser soldering technology can future-proof your production line and significantly enhance product quality and reliability. 🚀
✨ Conclusion
Laser soldering might seem like a niche technology now, but its adoption is growing rapidly. As machines become more affordable and easier to integrate, more manufacturers are making the switch.
If your business values precision, reliability, and scalability, laser soldering could be the competitive edge you’ve been looking for. 💼🔧

